ZYNQ SSE – Benchmark for the Xilinx ZC706
This Technical Brief shows how to setup the Zynq SSE. After going through the steps described herein, you will have a working Linux System running on the Zynq with an attached SATA HDD or SSD.
Copyright © 2026 Missing Link Electronics. All rights reserved. Missing Link Electronics, the stylized Missing Link Electronics MLE logo are the service mark and/or trademark of Missing Link Electronics, Inc. All other product or service names and trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
For the evaluation of Zynq SSE MLE supports two separate hardware platforms: The Avnet Zynq Mini-ITX board, and the Xilinx ZC706 Development Kit plus the XM104 Adapter Board. This document is for the Xilinx ZC706 plus XM104 Adapter Board.
MLE’s Zynq SATA Storage Extension (Zynq SSE) is a fully integrated and pre-validated system stack comprising 3rd-party SATA Host Controller and DMA IP cores from ASICS World Services, a storage micro-architecture from MLE, Xilinx PetaLinux, and an Open Source SATA Host Controller Linux kernel driver, also from MLE. Zynq SSE utilizes the Xilinx GTX Multi Gigabit Transceivers to deliver SATA I (1.5 Gbps), SATA II (3.0 Gbps), or SATA III (6 Gbps) connectivity.
The Zynq SSE is delivered as a complete reference design for the Xilinx Zynq-7000 All Programmable SoC (Zynq), and effectively extends Zynq with one single SATA host port for HDD and SSD storage connectivity.
This Technical Brief shows the Benchmark results you will see after correctly setting up the system as shown in the techtip: Zynq SATA Storage Extension.
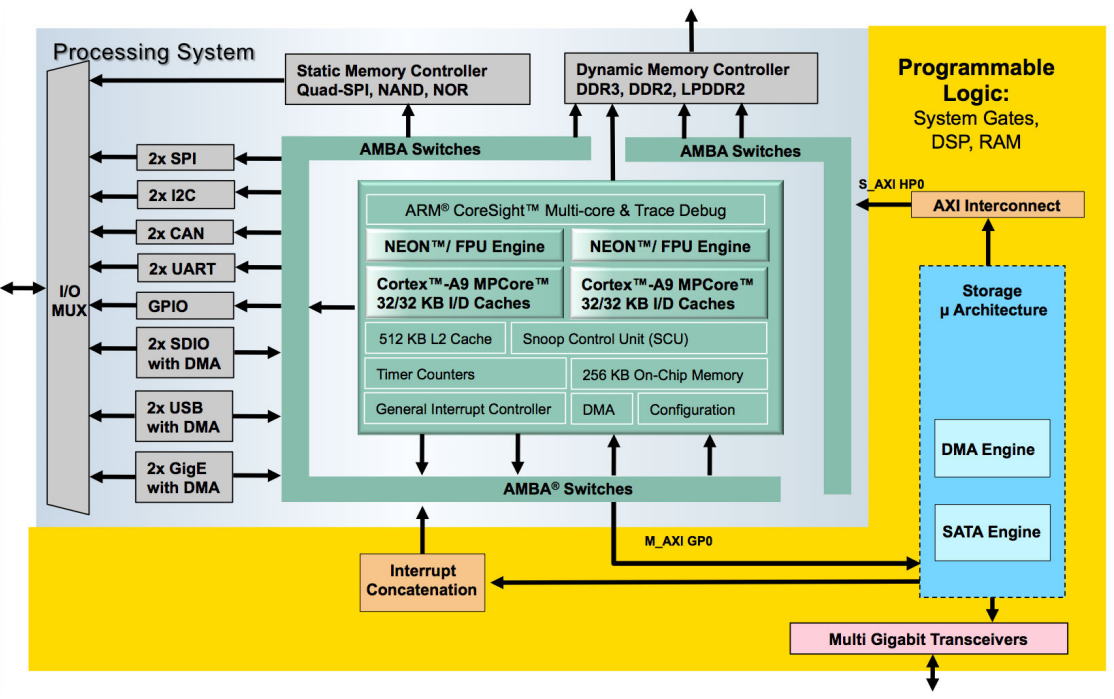
Block Diagram
The block diagram shown below gives an overview over the Zynq SSE reference design: Within the Zynq Programmable Logic (PL) the MLE storage micro-architecture instantiates the DMA and the SATA Host Controller IP blocks. The storage micro-architecture itself interfaces with the Zynq Processing System (PS) via the high-performance AXI HP0 slave port. The ARM A9 in the PS runs Xilinx PetaLinux and the SATA Linux kernel driver.
Implementation
| Implementation Details | |
|---|---|
| Design Type | PS + PL |
| SW Type | Linux (Petalinux) |
| CPUs | 2 CPUs 700 MHz |
| PS Features | DDR, USB, UART, ETHERNET |
| PL Cores | ASICS.WS SATA IP |
| Boards/Tools | ZC706, XM104 |
| Xilinx Tools Version | Vivado 2014.1, PETALINUX 2013-2 |
| Other Details | Samsung 840 SSD(including Cable and Power Supply), SD-Card |
| Address Map | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Base Address | Size | Interface | |
| SATA IP | 0x41000000 | 4K | S AXI |
| DMA IP | 0x41010000 | 4K | S AXI, M AXI |
| Files Provided | |
|---|---|
| BOOT.bin | Compilation of Bitstream, FSBL and U-Boot |
| Image.ub | Linux Ramdisk Image |
Step by Step Instructions
In front of Benchmarking the System, the Tech Tip “Zynq- Sata Storage Tech Tip” should be executed to have a working system. For Benchmarking the System, a tool called FIO is used. FIO is a tool that will spawn a number of threads or processes doing a particular type of I/O action as specified by the user. The typical use of FIO is to write a job file matching the I/O load one wants to simulate. We will now execute FIO with different Block sizes to see the impact on the Read and Write speeds of the system. Apply the following commands to the running SATA system, varying the Block size by using different values from 4k to 16M.
Read:
fio –ioengine=sync –direct=1 –rw=read –runtime=10 –filename=/dev/sda –size=1g –name=job1
–numjobs=4 –bs=4k
Write:
fio –ioengine=sync –direct=1 –rw=write –runtime=10 –filename=/dev/sda –size=1g –name=job1
–numjobs=4 –bs=4k
Expected Results
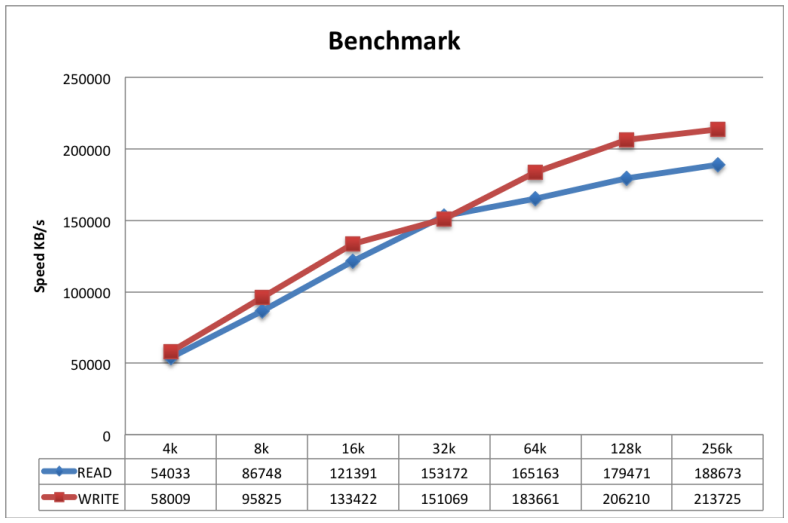
The user should see a Performance (given the right SSD) as shown in the Graph below:
Team MLE has spent significant efforts to try and test all aspects of Zynq SSE. If you feel that you encounter something not right, or if you do have any questions, please do not hesitate to contact us.
🌐 www.missinglinkelectronics.com
MLE (Missing Link Electronics) is offering technologies and solutions for Domain-Specific Architectures, which focus on heterogeneous computing using FPGAs. MLE is headquartered in Silicon Valley with offices in Neu-Ulm and Berlin, Germany.